Mechanism of Action of Oral Contraceptives
In the 21st century, women are equally educated and empowered to make their own decisions. They have the freedom to pursue their dreams and ambitions. Oral contraceptive pill is one of the most effective and easiest ways to family planning. With its high effectiveness, and its well-understood mechanism of action of oral contraceptives, OCP pill provides women with reliable control over their reproductive health.
Today, many married women successfully manage both their home and professional responsibilities. Moreover it is a convenient method of hormonal contraception. By understanding their mechanism of action and potential side effects, we can make informed decisions about choosing the right contraceptive for our needs.

Types of Birth Control Pills
There are two main types of birth control pills:
Combined Oral Contraceptives: These contain synthetic forms of two hormones, estrogen and progestin.
Progestin-Only Pills: Also known as minipills, these contain only progestin and no estrogen. They are particularly useful for women who cannot use estrogen for health reasons.
Choosing the right birth control pill depends on various factors, including:
- Menstrual situation
- Breastfeeding status
- Cardiovascular health
- Presence of other chronic diseases
- Other medications being taken
It’s essential to consult a doctor to determine the most suitable option for your health condition. When used correctly, birth control pills are 99% effective in preventing pregnancy. However, they do not protect against sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV. Buy contraceptives from trustworthy brand like Suvida.
How oral contraceptives work?
It is fact that many women are still unaware of how oral contraceptive pill works. The mechanism of oral contraceptive pill is easy to understand.
Oral contraceptives, commonly known as birth control pills, prevent pregnancy through various mechanisms depending on their type:
Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs)
Contain: Synthetic forms of two hormones, estrogen, and progestin.
Mechanism:
- Prevention of Ovulation: These hormones work together to inhibit the release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation).
- Thickening of Cervical Mucus: The pill thickens the mucus in the cervix, making it more difficult for sperm to enter the uterus and reach any egg that might be released.
- Thinning of Uterine Lining: The hormones also thin the lining of the uterus (endometrium), making it less likely for a fertilized egg to implant and grow.
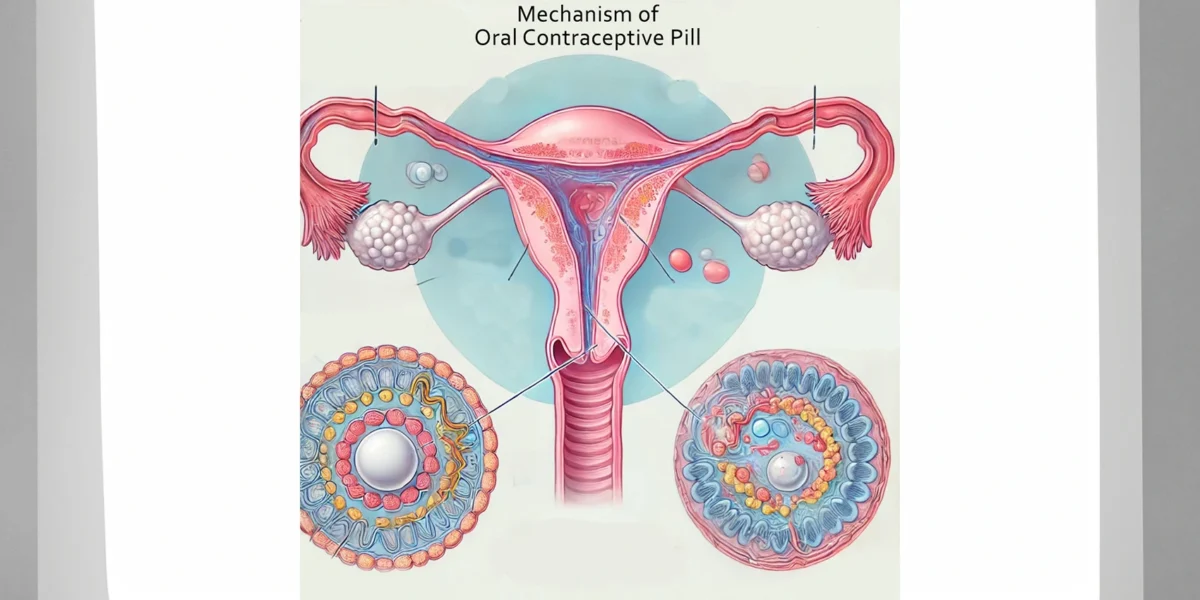
Progestin-Only Pills (POPs or Minipills):
Contain: Only the hormone progestin.
Mechanism:
- Thickening of Cervical Mucus: Similar to COCs, progestin-only pills thicken the cervical mucus to block sperm from reaching an egg.
- Suppression of Ovulation: In some women, progestin-only pills can also prevent ovulation, though this is not as consistent as with combined oral contraceptive pills.
- Thinning of Uterine Lining: Like COCs, these pills thin the endometrial lining, reducing the likelihood of implantation.
Check oral contraceptives pills review before buying.
Wrapping up
Oral contraceptive pills offer women an effective and convenient method for family planning in india and controlling their reproductive health. By understanding the different types of pills and their mechanisms of action, women can make informed choices that best suit their individual health needs. Remember, while highly effective in preventing pregnancy, birth control pills do not protect against sexually transmitted diseases. For trusted options, consider reputable brands like Suvida.
Oral contraceptives contain two types of hormones- estrogen and progestin.
Estrogen and progestin work together to prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and thin the uterine lining.
Oral contraceptives thin the lining of the uterus (endometrium), making it less suitable for implantation.
Oral contraceptives prevent ovulation by inhibiting the release of eggs from the ovaries.
Thickened cervical mucus blocks sperm from entering the uterus and reaching an egg.
No, combined oral contraceptives and progestin-only pills have different mechanisms and hormone compositions.
Oral contraceptives typically begin to work within seven days if started at the beginning of a menstrual cycle.
Yes, oral contraceptives regulate, lighten, or sometimes eliminate menstrual cycles.
Low-dose contraceptives have fewer side effects but may be less effective at suppressing ovulation compared to high-dose pills. Suvida is a low dose and effective oral contraceptive pill.
Missing a dose can reduce effectiveness and may require backup contraception or emergency contraception.
Oral contraceptives, patches, and rings all prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and thin the uterine lining.
No, the mechanism of action of oral contraceptives doesn’t affect bone health or any other health hazards.
